WHAT IS COCHLEAR IMPLANT
A cochlear implant is a medical device that is surgically implanted into the inner ear to provide a sense of sound to individuals with severe to profound hearing loss. Unlike hearing aids, which amplify sounds, cochlear implants work by directly stimulating the auditory nerve inside the cochlea, the spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear responsible for hearing.
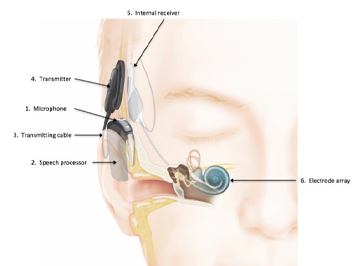
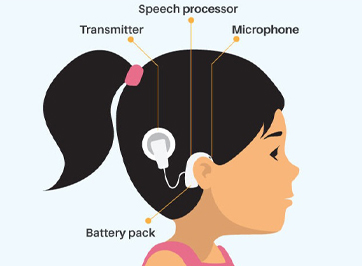
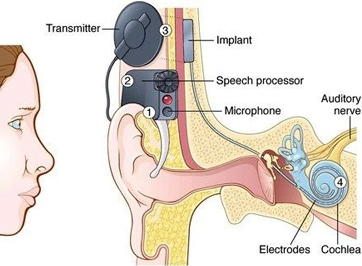
Microphone and Speech Processor
The processed digital signals are sent to a transmitter coil worn on the outside of the head. This transmitter sends the signals through the skin to an internal receiver/stimulator, which is surgically implanted under the skin behind the ear.
Transmitter and Receiver
The external component of the cochlear implant consists of a microphone that picks up sounds from the environment. These sounds are then processed by a speech processor, a small wearable device that converts the sound into digital signals.
Electrode Array
The receiver/stimulator decodes the signals and sends them to an electrode array, a group of electrodes that are inserted into the cochlea during the surgical procedure. These electrodes stimulate the auditory nerve fibers directly.
Brain Interpretation
The stimulated auditory nerve fibers send signals to the brain, where they are interpreted as sound. Over time, the brain learns to interpret these electrical signals as meaningful sounds, allowing the individual to perceive speech, environmental sounds, and other auditory cues.
Contact us to know more about implant and its candidacy. We will help to assess the candidacy criteria , educate you on the procedures. We provide cochlear implant mapping services and other accessories for cochlear implant